The stationary energy storage market is growing fast, both Front-of-the-Meter (FTM) and Behind-the-Meter (BTM), with the market size expected to be tens of billions by 2031 and largely dominated by Li-ion batteries. However, IDTechEx in its latest report, Batteries for Stationary Energy Storage 2021-2031, believes that the stationary storage market is still in its early stages, and there is still time for other technologies to have an impact.
One of the messages of the report is that every country has its own approach toward the necessary adoption of energy storage systems, which could be in focusing on the behind-the-meter applications, or developing large battery storage systems.
Only in 2020 have projects been announced for the next few years for about 5GWh of energy stored. Although the large majority of these installations are Li-ion batteries, other technologies are also approaching the market.
Redox Flow Battery:
The Redox Flow Battery, or RFB, is an electrochemical secondary battery base on the two electroactive species dissolved in liquids electrolytes, which are circulated from a reservoir (tank) to the electrochemical reactors (stack), and back to the reservoir by means of pumps. The main characteristics of the flow batteries are decoupled energy/power capacity and a long lifetime.

These two characteristics make the RFB well suited to store a large amount of energy, far above the typical 4h of storage. RFB companies are targeting the 6h to 12h hours of storage. The technology is currently a step behind Li-ion but is now ready for large installations. IDTechEx has followed this technology and its development, publishing a separate report ‘Redox Flow Battery 2021-2031’. The report’s analysis pf the future adoption of RFB systems, shows the possibility of fast growth over the next decade, and that they may overtake the Li-ion battery systems in terms of energy capacity installed.
Long Duration Energy Storage (LDES):
Long duration energy storage systems, analysed by IDTechEx in the report “Stationary Energy Storage Without Batteries: Grid, Microgrid, UPS, Trackside 2021-2041”, are devices able to store large amounts of energy for a duration that ranges from tens of hours to days. These systems are generally based on a simple working principle, such as lifting a weight (Gravitational Energy Storage), or pumping water uphill (Pumped Hydro Energy Storage). Although these systems might find larger applications toward the end of 2030, when a larger renewable energy amount will be installed, up to date the application of these devices is still quite limited. The main reason is because of their small market, due to their reduced application, but soon some of these systems (like compressed air energy storage (CAES), liquified air energy storage (LAES) and potentially also the gravitational energy storage systems (GES)) might start to face larger adoption.
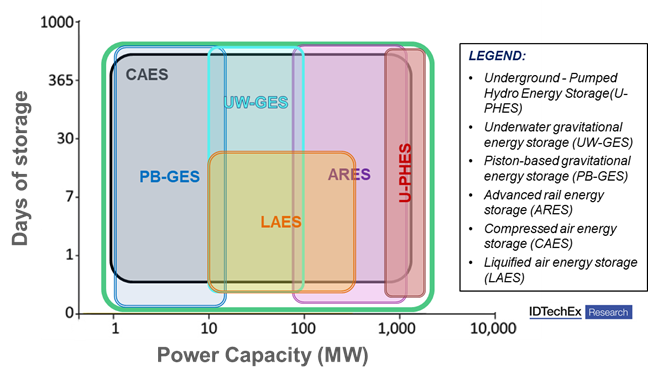
The stationary storage market is evolving with increasing differentiation from in the duration of storage and application BTM and FTM. Overall, the market will still be driven by two main factors: the penetration of renewable energy and the flexibility of the power grid.
For more information on these reports available from IDTechEx click here.



